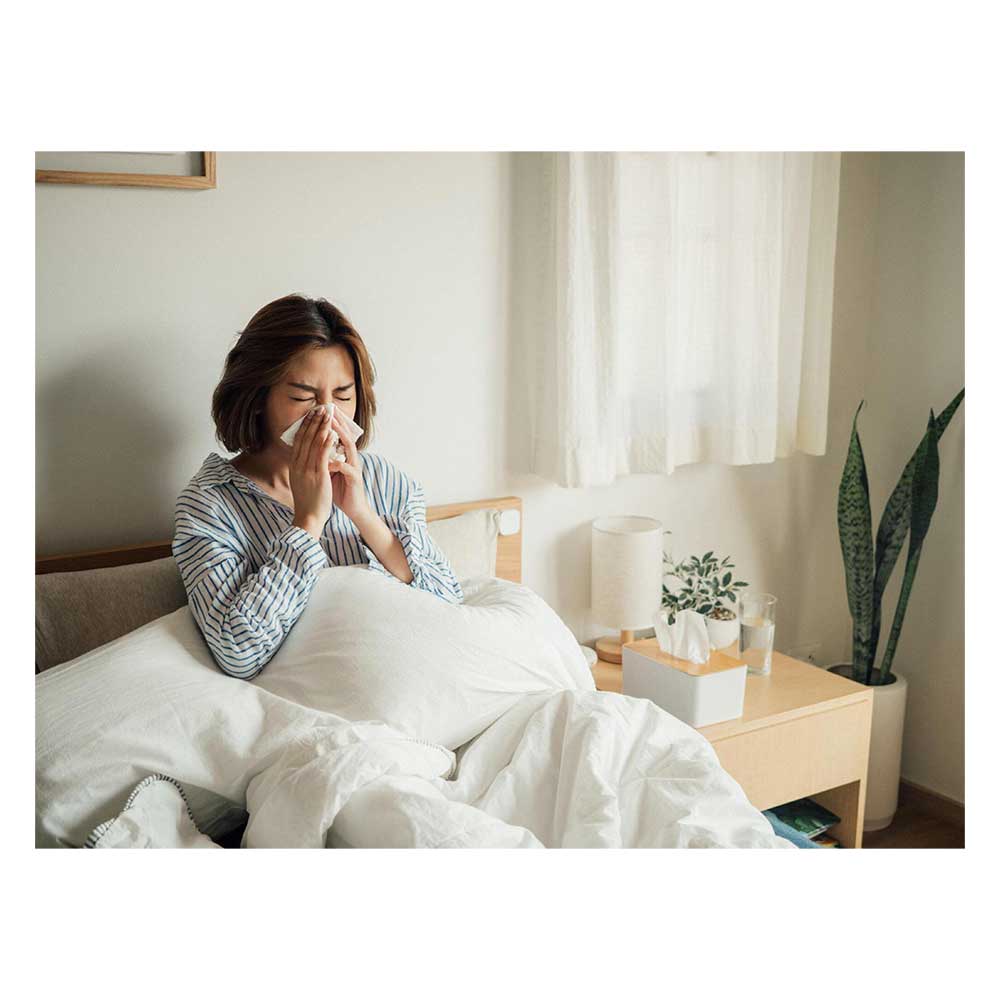
Allergic Rhinitis, commonly referred to as hay fever, is an immune system reaction affecting the nasal passages, triggered by seemingly harmless substances such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or mold spores. This condition manifests through symptoms like sneezing, nasal congestion, itching, and watery eyes, which can significantly impact daily life.
Symptoms Overview
Allergic Rhinitis typically presents with:
- Frequent sneezing
- Nasal congestion or a runny nose
- Itching in the throat or nasal passages
- Watery eyes
These symptoms can lead to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, disrupting daily activities and overall quality of life.
Causes
Allergic Rhinitis arises from an exaggerated immune response to allergens. When exposed to triggers, the body produces antibodies, which then prompt the release of histamines and other chemicals, leading to the characteristic symptoms.
Treatment Approaches
Managing Allergic Rhinitis involves a combination of environmental control, lifestyle adjustments, and medication.
Environmental Control
To manage allergens effectively:
- Identify and minimize exposure to known triggers.
- Use air purifiers and ensure proper ventilation to reduce indoor allergens.
- Regularly clean living spaces to minimize allergen buildup.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Implementing lifestyle changes can significantly reduce symptoms:
- Use allergen-resistant bedding to minimize exposure during sleep.
- Keep windows closed during high pollen seasons to prevent outdoor allergens from entering the home.
- Shower after outdoor activities to wash off pollen and allergens.
Medication
Various medications can help control the symptoms of Allergic Rhinitis:
- Antihistamines: Over-the-counter options like cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine help counteract the effects of histamine, reducing itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
- Decongestants: Medications such as pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine relieve nasal congestion but should be used cautiously, especially by individuals with hypertension.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: Sprays like fluticasone, budesonide, and mometasone reduce nasal inflammation and are effective for long-term management.
- Leukotriene Inhibitors: Montelukast helps control symptoms by blocking leukotrienes’ action and is often used alongside other medications.
- Immunotherapy: Allergy shots or sublingual tablets aim to desensitize the immune system to specific allergens over time, which is particularly beneficial for severe allergies.
Metrogyl Gel in Allergic Rhinitis
Metrogyl Gel, which contains metronidazole, is primarily an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is not a standard treatment for Allergic Rhinitis and should not be used for this condition without consulting a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Allergic Rhinitis can be effectively managed through a comprehensive approach involving environmental control, lifestyle modifications, and various medications. Antihistamines, decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, and immunotherapy play crucial roles in alleviating symptoms and improving overall well-being for individuals suffering from Allergic Rhinitis. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms early, and implementing effective management strategies, individuals can lead healthier, more comfortable lives despite this chronic condition.